Hip And Knee Joint Replacement
Hip And Knee Joint Replacement
Hip and knee joint replacements have become increasingly common medical procedures, providing relief to individuals experiencing debilitating symptoms. Understanding the symptoms that indicate the need for joint replacement and the considerations involved in this process is crucial for those seeking improved mobility and a better quality of life. Just as navigating the world of joint health is important, exploring neue online casinos can also be an exciting and rewarding experience. If you’re ready for a different kind of thrill, consider visiting it, where you might find entertainment that complements your journey filled with games to enhanced well-being.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of Hip Joint Issues:
-
Persistent Pain: One of the primary symptoms prompting hip joint replacement is persistent pain. This pain often occurs during activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or even while resting.
-
Limited Range of Motion: Individuals with hip joint problems may experience a reduced range of motion. Difficulty in moving the hip joint can significantly impact daily activities and overall flexibility.
-
Stiffness and Discomfort: Stiffness in the hip joint, accompanied by discomfort, can be indicative of joint degeneration. This may be particularly noticeable after prolonged periods of inactivity.
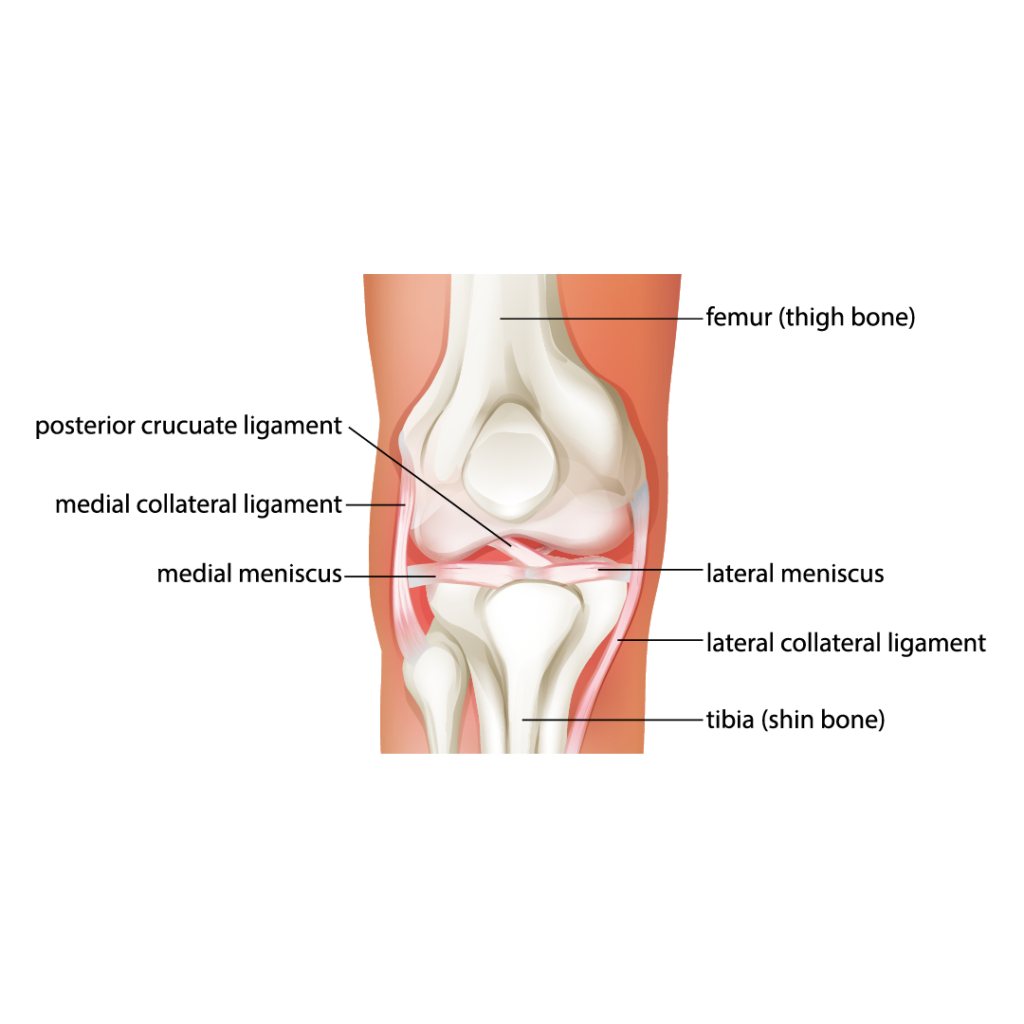
Symptoms of Knee Joint Issues:
-
Chronic Knee Pain: Ongoing knee pain, especially during weight-bearing activities, can signal the need for knee joint replacement. This pain may hinder daily tasks and compromise the individual’s overall quality of life.
-
Swelling and Inflammation: Persistent swelling and inflammation around the knee joint are common symptoms of joint degeneration. This can lead to discomfort and may affect the joint’s stability.
-
Difficulty in Walking: Individuals with deteriorating knee joints often find it challenging to walk without pain. This limitation in mobility can impact independence and daily activities.
Considerations for Joint Replacement:
-
Medical Evaluation: Before opting for joint replacement, a thorough medical evaluation is essential. This typically includes imaging studies, such as X-rays and MRIs, to assess the extent of joint damage.
-
Non-Surgical Interventions: In some cases, non-surgical interventions like physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications may be recommended initially to manage symptoms. However, if these prove ineffective, joint replacement might be considered.
-
Choosing the Right Time: Deciding when to undergo joint replacement is a crucial consideration. It is often recommended when the pain and limitations significantly impact the individual’s daily life, and conservative treatments no longer provide relief
-
Rehabilitation and Recovery: Understanding the rehabilitation and recovery process is vital. Following joint replacement, individuals undergo physical therapy to regain strength and mobility. Full recovery may take several weeks to months.
Treatment:
Conservative Treatments:
Physical Therapy:
- Physical therapy plays a crucial role in improving joint function and reducing pain.
- Targeted exercises help strengthen the muscles surrounding the hip and knee joints, enhancing stability and flexibility.
Medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can alleviate pain and reduce inflammation in both hip and knee joint issues.
- Pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, may be recommended to manage discomfort.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight management is essential, as excess weight can exacerbate joint problems. Adopting a healthy diet and exercise routine can positively impact joint health.
Assistive Devices:
- Canes, braces, and orthopedic footwear may be prescribed to provide support and alleviate pressure on affected joints.
Advanced Interventions:
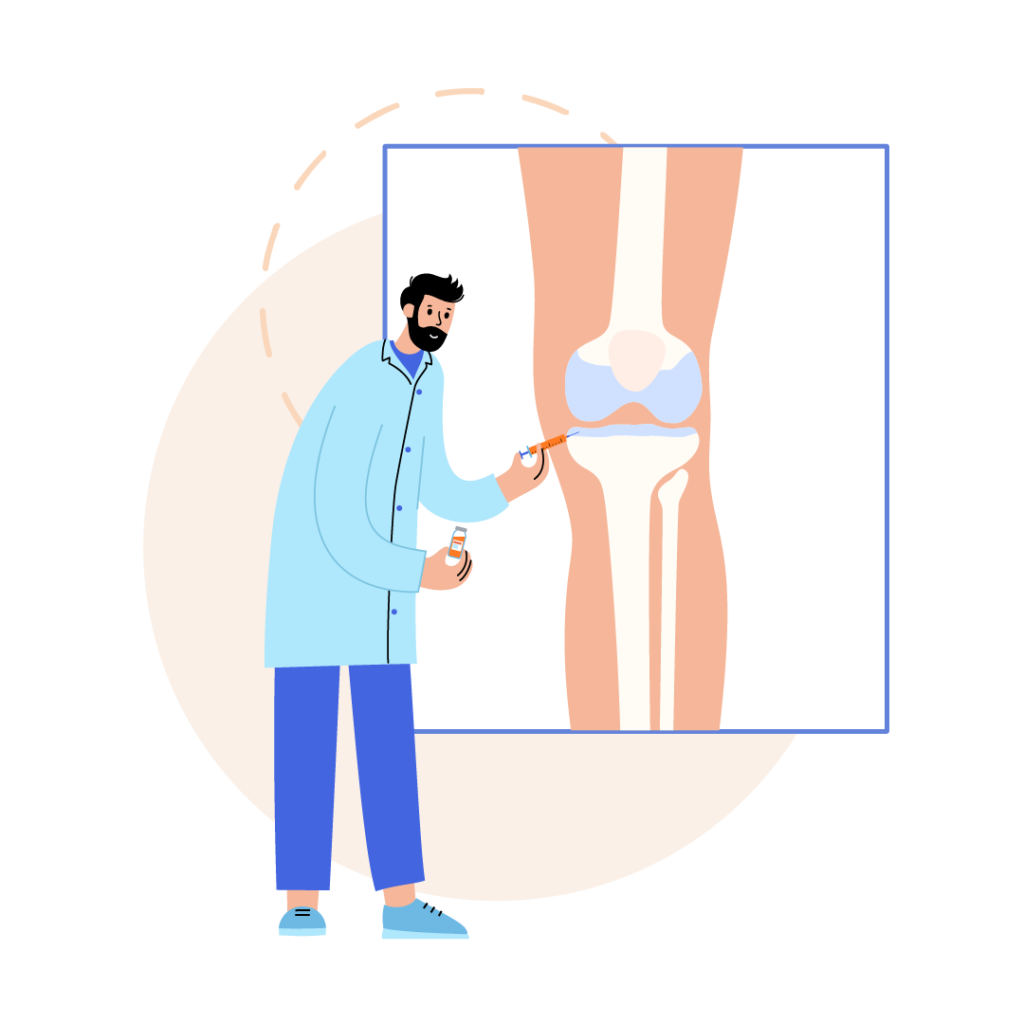
Corticosteroid Injections:
- Injections of corticosteroids directly into the joint can provide temporary relief from inflammation and pain.
Viscosupplementation:
- This involves injecting a gel-like substance into the joint to improve lubrication and reduce friction, particularly in knee joint issues.
Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that allows for the inspection and treatment of joint issues through small incisions.
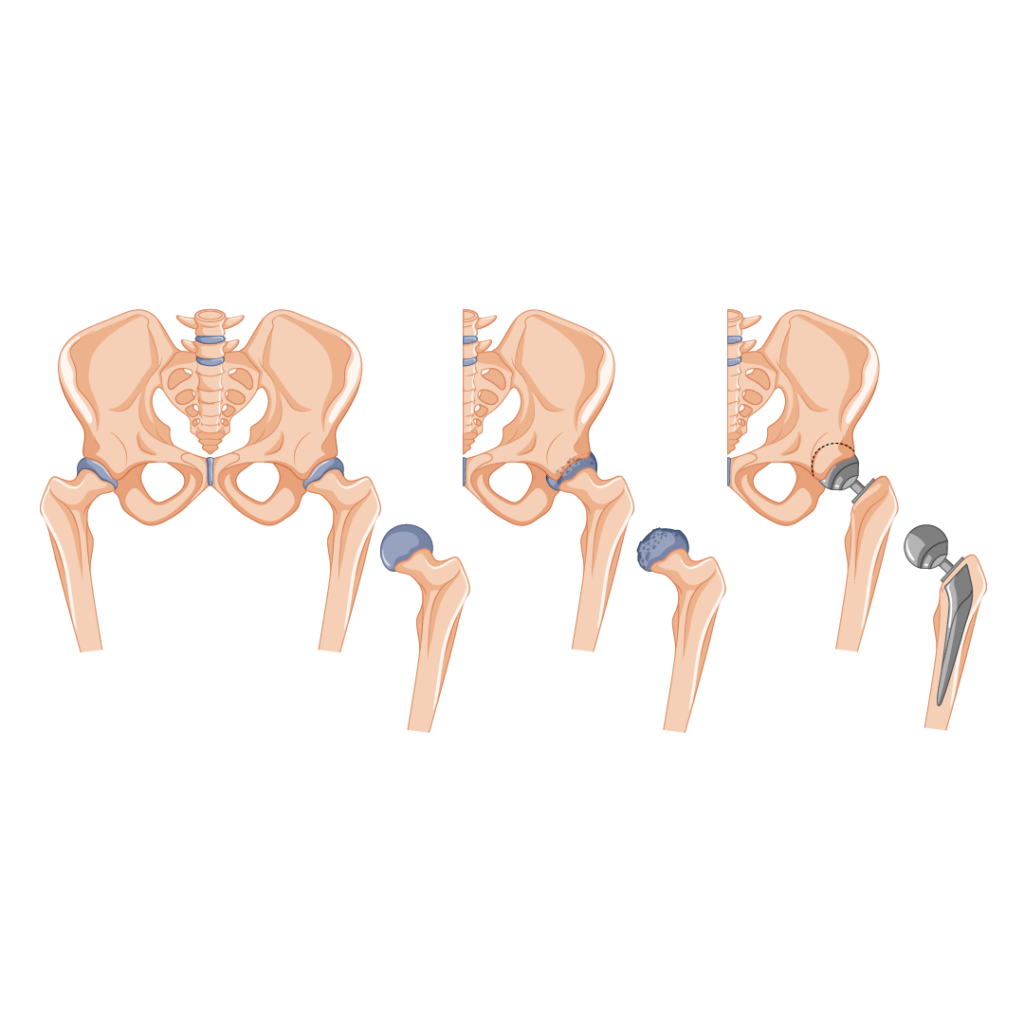
Surgical Options:
Joint Replacement Surgery:
- Total hip or knee joint replacement is considered when conservative measures no longer provide relief.
- High-quality artificial joints are used to replace damaged ones, restoring function and reducing pain.
Osteotomy:
- In cases of knee joint issues, osteotomy may be performed to realign the bones and relieve pressure on the damaged area.
Joint Fusion (Arthrodesis):
- This surgical procedure involves fusing the joint surfaces to eliminate movement, often considered in specific cases of severe arthritis.
Post-Treatment Rehabilitation:
Physical Rehabilitation:
- Following surgical interventions, physical therapy is essential to regain strength, flexibility, and mobility.
- Rehabilitation protocols are tailored to the specific procedure and individual needs.
Pain Management:
- Medications and other pain management techniques are employed post-surgery to ensure a comfortable recovery.